
Search behavior has changed more in the past 18 months than in the last decade.
Users are no longer just typing queries into Google and scrolling through blue links.
They’re asking ChatGPT to summarize, using Perplexity to research, and relying on AI-generated answers to make decisions without ever clicking through to a traditional website.
This shift is not theoretical, it’s already visible in the numbers.
In June 2025, Google’s global search market share dropped to 89.54%, marking its first significant decline in over 10 years.
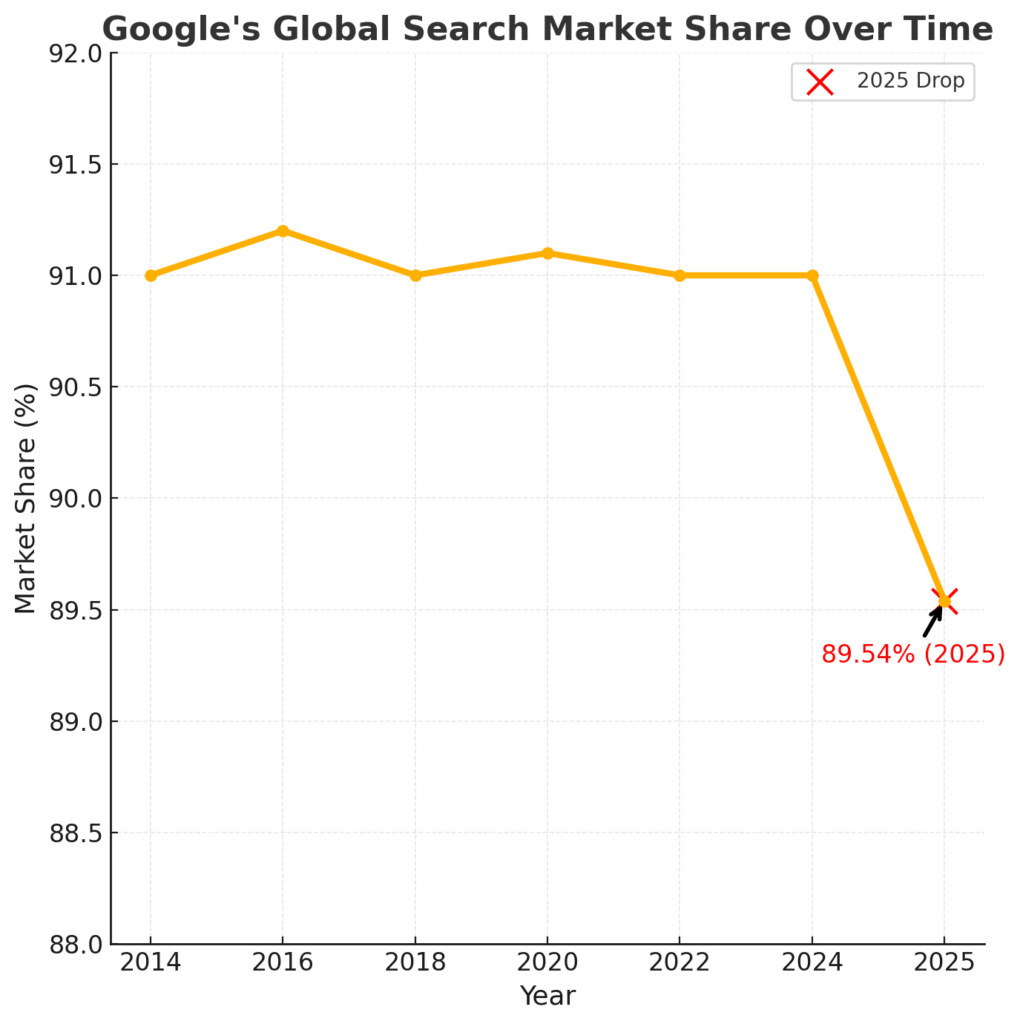
Meanwhile, zero-click searches now account for 58.5% of all U.S. queries, meaning the majority of users never even reach a publisher’s page. At the same time, traffic from large language model (LLM) platforms like ChatGPT and Perplexity has grown eightfold since early 2024, reflecting an aggressive and irreversible shift in where discovery is happening.
The implications are massive for content creators, marketers, and SEO professionals.
Ranking in the top 10 is no longer the primary goal. Being referenced, summarized, and quoted by AI systems is becoming the new visibility currency.
This emerging landscape requires a different approach, one that prioritizes semantic depth, entity clarity, and structured content built for how LLMs parse and present information.
In short, it requires a new discipline:
LLM SEO or you can say AI SEO.
In this guide, we’ll break down what LLM SEO really means, why it matters now more than ever, and how you can optimize your content to thrive in an AI-driven search environment before your competitors catch up.
The AI Shift in Search: Why Traditional SEO Is No Longer Enough
Search is no longer about matching keywords. It’s about understanding meaning and delivering answers before users ever click.
Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4, Gemini, and Claude have fundamentally changed the way content is retrieved, ranked, and presented.
Instead of displaying ten blue links, today’s AI-powered search systems interpret entire topics, extract key concepts, and generate summaries or direct responses. This shift marks the beginning of the end for traditional SEO tactics.
From Keywords to Concepts: The LLM Paradigm
In the LLM era, relevance isn’t determined by keyword frequency, it’s defined by semantic relationships, entity coverage, and contextual depth.
LLMs don’t “crawl and index” the same way classic search engines do. They rely on vector embeddings, knowledge graphs, and passage-level comprehension to decide which content is most useful not just which is most optimized.
This is why tactics like keyword stuffing, basic H1 optimization, or even conventional on-page best practices are rapidly losing ground.
86% of SEO professionals have already integrated AI tools into their strategy, and 68% have reallocated budget specifically toward improving visibility in AI-powered search environments.
To compete today, your content must not just rank but it must be understood by machines and referenced in real-time language generation.
This is the essence of LLM SEO: optimizing your content not just for discovery, but for citation inside generative search responses.
Google SGE, Gemini, and the End of Ranking As We Knew It
The introduction of Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) and its Gemini LLM integration signals a clear direction: users will increasingly see AI-generated answers first, not organic listings.
That means the top 10 rankings are no longer the gateway to traffic.
SGE combines LLM summarization with traditional search results but it does so by pulling from specific passages within high-quality, topically authoritative content. These passages are often quoted inline, reducing the need for users to click through at all.
And Gemini’s growing capabilities especially its integration with AI Overviews further prioritize content that is structured, concept-rich, and machine-readable.
At the same time, traditional publishers are already seeing the downside. Publisher traffic has declined 27% year-over-year since February 2024, largely due to AI models replacing click-through behavior with summarized answers.
This isn’t a minor update to the algorithm. It’s a paradigm shift in how information flows from creators to users.
Misconceptions About AI Search and What’s Actually Happening
Many marketers still think AI search will eventually “pass” and that traditional SEO will rebound.
But that’s not what the data shows.
Here’s what’s actually happening:
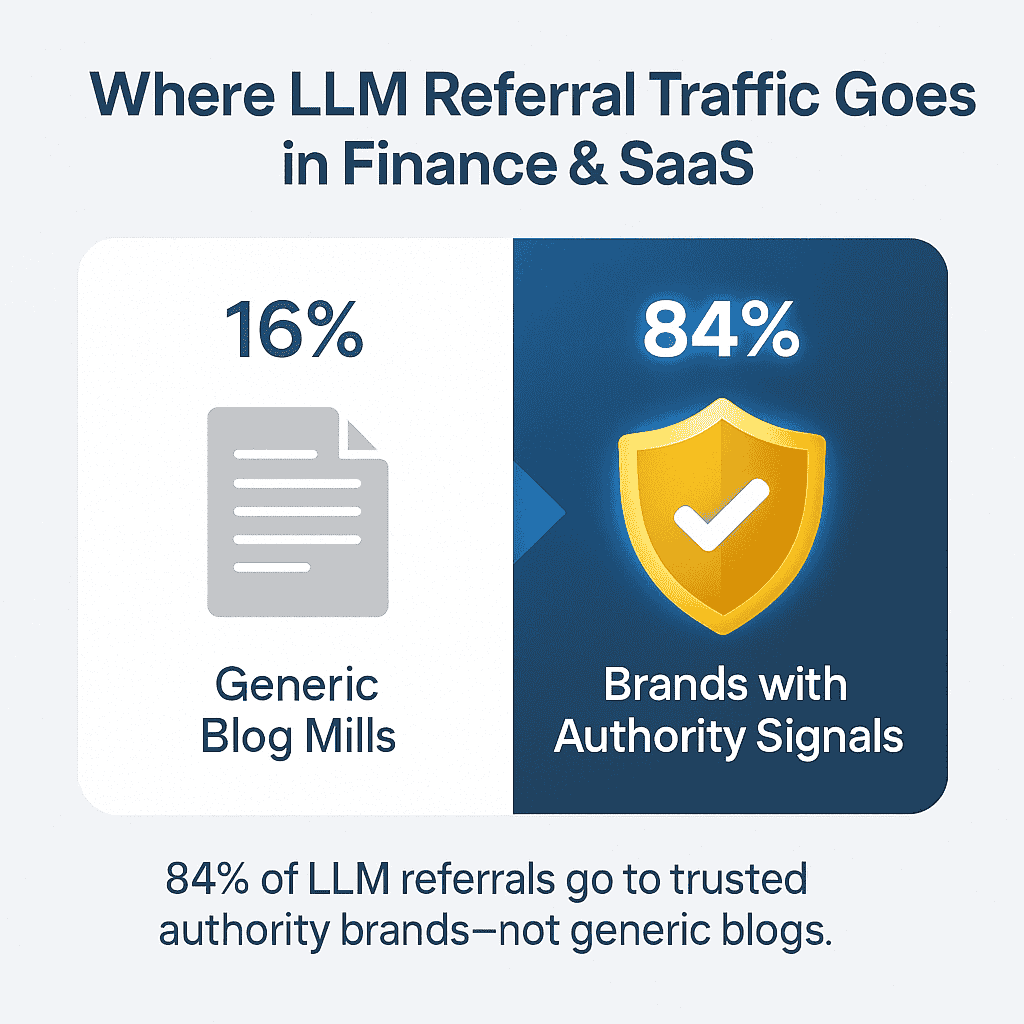
- LLM referral traffic is real and rising. Platforms like ChatGPT and Perplexity now account for a growing share of total discovery traffic commanding 37% each of LLM-driven referrals.
- LLM users are 4.4x more valuable than traditional organic search visitors, signaling stronger engagement and conversion behavior.
- Zero-click behavior is becoming the norm, not the exception. More than half of all U.S. searches never result in a click and that number is growing as AI responses get better.
What this means is clear:
Optimizing for AI visibility is no longer optional. It’s the difference between being found and being forgotten.
What Is LLM SEO? Understanding the New Search Landscape
As large language models (LLMs) take center stage in search.
This isn’t a rebrand of traditional SEO, it’s a fundamentally different way of optimizing content. Instead of aiming to rank in a list of links, LLM SEO is about being referenced, summarized, and quoted inside AI-generated answers.
Let’s break it down.
Defining Large Language Model (LLM)-Driven SEO
LLM SEO is the practice of structuring and optimizing content so that it is easily understood, cited, and surfaced by AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity AI, Gemini, and Claude.
Unlike traditional search engines, which rely on indexed pages and link-based ranking signals, LLMs work by:
- Parsing language and meaning through vector embeddings
- Understanding relationships between entities, not just keywords
- Recalling relevant content from training data or plugins in real time
- Generating answers based on semantic relevance, not position on a SERP
In this model, visibility comes not from your page title or backlinks but from how well your content aligns with what the LLM understands and wants to surface.
A recent study showed that 80% of users rely on AI-powered summaries at least 40% of the time, and 68% use LLMs specifically for research and information gathering. In this new reality, being cited by an AI model may matter more than being ranked by Google.
LLM SEO is about optimizing for that visibility window.
How LLMs Interpret, Summarize, and Surface Content
To optimize for LLMs, you must first understand how they “think.”
Large language models don’t index websites in the same way search crawlers do.
Instead, they ingest vast corpora of data (web pages, books, Wikipedia, documentation), convert that data into vectorized representations, and generate outputs by predicting the most probable next word or sentence based on user intent.
When a user asks a question like “What’s the best content strategy for SaaS?”, an LLM doesn’t serve a link. It generates a summary or direct answer, often pulling from passage-level content it deems most semantically aligned.
Key LLM content triggers include:
- High semantic density (rich explanations using clear concepts)
- Strong entity coverage (mentioning related terms, tools, people, industries)
- Clear structure (headers, FAQs, definitions, bullet points)
- Authoritativeness and clarity, not just word count
This is why concepts like passage ranking SEO, semantic SEO for LLMs, and entity optimization are now at the heart of modern search strategy.
Key Differences from Classic SEO Tactics
Here’s how LLM SEO breaks from the traditional playbook:
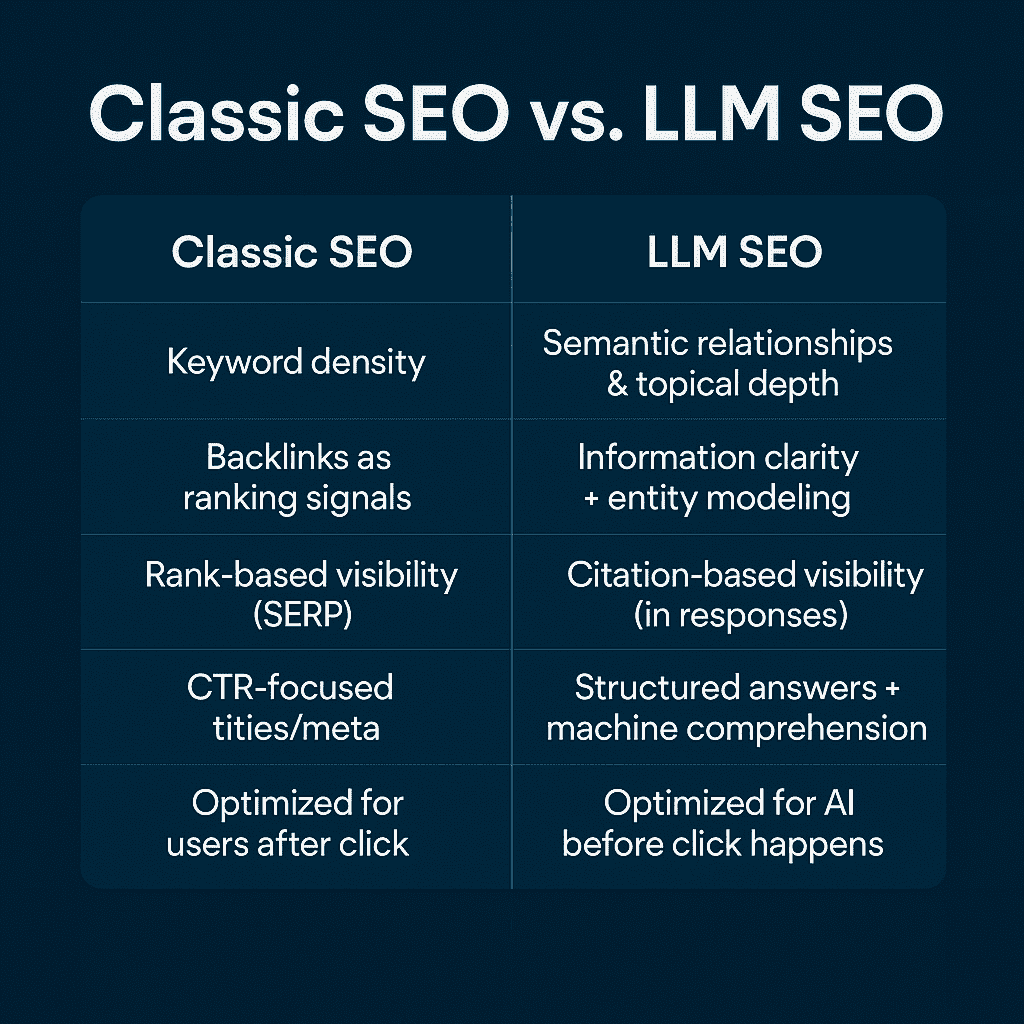
With traditional SEO, the goal is traffic. With LLM SEO, the goal is influence to shape the AI-generated response.
That’s why LLM SEO strategy isn’t about increasing volume, but improving LLM recall, answer inclusion, and semantic authority.
The LLM SEO Framework: Optimizing for Meaning, Not Just Keywords
LLM SEO isn’t about chasing rankings. It’s about designing content that machines understand and humans trust.
As search shifts from keyword matching to meaning extraction, traditional SEO tactics alone fall short. To be cited by large language models like Gemini, ChatGPT, and Perplexity, your content needs to be semantically rich, structurally clear, and contextually aligned with AI intent.
Here’s the full framework to optimize for LLM visibility, AI summarization, and zero-click discovery.
1. Semantic Entity Optimization
Traditional SEO focused on keywords; LLM SEO is built on entities and relationships.
Entities are the foundational concepts, people, brands, and topics your content must mention to be seen as authoritative on a subject. For example: A post about “Passage Ranking SEO” should also reference “Google SGE,” “semantic SEO,” “vector embeddings,” and “AI search engine architecture.”
Practical Tip:
- Use tools like Google’s Natural Language API, InLinks, or MarketMuse to analyze and expand your entity coverage.
- Map all related subtopics, synonyms, and adjacent concepts in your content outline.
- Example: If optimizing for “LLM SEO”, ensure your page also covers “large language models,” “semantic search,” “content optimization for AI,” and “passage-level ranking.”
2. User Intent Mapping and Predictive Search
LLMs thrive on intent, not just explicit queries. They anticipate what a user wants next and surface answers to related questions before the user asks.
Strategy:
- Map the primary, secondary, and latent intents behind every target keyword.
- Build content that answers related questions, solves adjacent problems, and links out to deeper resources.
- Example: For “best LLM SEO strategy,” include answers to “how do LLMs rank content,” “what makes content citation-worthy for AI,” and “how do I optimize for zero-click search?”
Pro Tip:
- Integrate tools like AlsoAsked or AnswerThePublic to visualize follow-up intent branches.
- Predict and preempt user queries with FAQ sections, internal links, and resource round-ups.
3. Contextual Content Structuring
Structure is now a ranking factor. LLMs perform best with clean, modular, and contextually rich content.
Action Steps:
- Break down content with logical H2/H3s using keyword + entity blends (e.g., “Semantic SEO for LLMs: Best Practices”).
- Keep paragraphs short ideally 2–4 sentences each.
- Use bullet lists, call-out boxes, tables, and sidebars to make information modular.
- Example: If explaining “vector embedding SEO,” start with a concise definition, then show a visual, and end with a quick FAQ.
Advanced Tip:
- Add schema-driven sections (“Pros and Cons,” “Step-by-Step Guide”) to help LLMs parse each intent clearly.
4. Passage-Level Relevance and Topical Authority
LLMs quote passages, not pages. Every paragraph is a possible citation.
How to Win:
- Craft each section to be “self-contained” meaning, it fully answers a specific question on its own.
- Add stats, definitions, analogies, and micro-examples in each subsection.
- Example: A short block explaining “passage ranking SEO” should directly define the term, provide a real-world example, and offer a citation-worthy insight all in 3–5 sentences.
Fact:
- With Google SGE, 3-5 unique passages are typically cited per AI Overview, so each block is a chance to “win” an inclusion.
5. Conversational AI Content Optimization
AI-generated answers sound human your content should too.
Best Practices:
- Write in natural, clear language that mirrors user intent (“How do I…” “What happens if…”).
- Use conversational transitions (“In simple terms…” “Let’s break this down…”).
- Directly address the reader (“You’ll notice…” “Here’s what matters…”).
- Example: When explaining “semantic SEO for LLMs,” say: “Think of LLMs as supercharged librarians. They don’t just count keywords, they map every topic you cover and how clearly you explain it.”
Bonus:
- Add short story snippets, analogies, or rhetorical questions to boost citation potential and user engagement.
6. Structured Data and Schema Implementation
Schema markup is your bridge between content and machine comprehension.
How to Use:
- Mark up your FAQs, definitions, How-Tos, reviews, and product details using JSON-LD or in-page schema.
- Prioritize “FAQPage”, “HowTo”, “Article”, and “Breadcrumb” schema for service and blog content.
- Add entity-focused schema (Organization, Person, Product) to clarify relationships for LLMs.
Real-World Example:
- Google and Gemini use schema to identify key content for “AI Overviews” and instant answers often elevating structured data above regular text.
Tool:
Schema.org and plugins like Merkle Schema Generator.
7. Content Authority and E-E-A-T Optimization
Trust is the new ranking factor both for Google and AI models.
How to Build E-E-A-T:
- Add author bios, credentials, and real client results.
- Use first-party data and cite credible sources throughout.
- Publish expert interviews, proprietary research, and testimonials.
- Reference partnerships, press coverage, and industry certifications.
Micro-Insight:
8. Zero-Click Search Strategy and Optimization
AI search means users get answers instantly often without clicking.
Tactics to Win:
- Write “definition-first” sentences: “LLM SEO is the practice of…”
- Create quick-reference tables, TL;DR blocks, and summary callouts at the top of articles.
- Use FAQ and “Did You Know?” snippets.
- Example: At the top of a pillar page, add Stats.
Remember, 58.5% of all U.S. searches are now zero-click so optimize for AI inclusion, not just organic traffic.
9. LLM-Specific Content Formatting and Structure
LLMs are trained on patterns. The clearer your structure, the higher your inclusion odds.
Frameworks:
- Use TEACH (Tell, Explain, Apply, Compare, Help), CLEAR (Context, Lead-in, Examples, Actions, Recap), and PROOF (Point, Reason, Outcome, Obstacle, Fix) to design each block.
- Bold or highlight main ideas at the start of each section.
- Place key stats and definitions in the opening 200–300 words.
Example:
For “Passage Ranking SEO,” use:
- H2: What Is Passage Ranking SEO?
- Short definition
- One real example
- 3-point checklist
- Mini-case or analogy
10. Technical SEO for AI Crawling and Processing
LLMs might not crawl, but good technical SEO future-proofs your site.
Steps:
- Ensure fast load times, mobile-first design, and no intrusive interstitials.
- Validate clean HTML/CSS LLMs and classic crawlers both prefer “readable” code.
- Use descriptive alt text, logical URL structures, and XML sitemaps for crawlability.
- Keep pages indexable (unless intentionally noindexing for privacy or duplicate control).
Advanced:
Monitor Core Web Vitals and Lighthouse scores—even AI platforms may weigh UX metrics in the future.
11. Multi-Platform LLM Optimization Strategy
Every LLM has unique ranking signals. Don’t optimize for just one.
How to Diversify:
- For ChatGPT: Provide concise, expert answers and use authoritative linking.
- For Perplexity: Write modular content with clear citations and up-to-date sources.
- For Gemini: Prioritize AI Overview-friendly structures FAQs, bullet lists, and TL;DRs.
- For Claude: Focus on thorough, fact-checked long-form and explanatory tone.
Practical Tip:
Repurpose one in-depth blog into multiple platform-friendly chunks summaries for ChatGPT, deep dives for Gemini, interactive Q&A for Perplexity.
Stat:
- In May 2025, ChatGPT and Perplexity each controlled ~37% of all LLM referral traffic. Diversification is no longer optional it’s survival.
- LLM SEO is about building content that educates, persuades, and stands out both to machines and to the people they serve.
Implementing LLM SEO: Step-by-Step Execution Plan
LLM SEO isn’t a one-time fix, it’s a new way of building, optimizing, and future-proofing content. Here’s how to roll it out, step by step:
Step 1: Conducting Semantic Topic Research
The foundation of effective LLM SEO is semantic topic research going beyond keywords to map out the entities, concepts, and intent branches your audience (and LLMs) care about.
How to Execute:
- Use tools like MarketMuse, InLinks, or Google’s NLP API to analyze top-ranking and AI-cited content.
- Identify not just keywords, but all related entities (people, tools, industries, processes).
- Map out topic clusters and their relationships (e.g., “LLM SEO,” “semantic SEO for LLMs,” “passage ranking,” “vector embedding SEO,” “entity optimization”).
- Analyze competitor content that appears in Google SGE or is referenced in LLM answers.
Actionable Tip: Build a content map that covers core topics and expands into long-tail, entity-rich subtopics. This ensures your content is discoverable by both Google’s SGE and LLM-powered tools.
Step 2: Creating Content That Answers Predictive Intents
Traditional SEO content answers a keyword; LLM SEO content answers a conversation.
How to Execute:
- Predict user intent branches: Start with the primary query, then list follow-up and adjacent questions users are likely to ask.
- Build modular content sections for each predictive intent (“What is LLM SEO?”, “How do LLMs rank content?”, “What’s the best passage-level strategy?”).
- Incorporate FAQ sections and “People Also Ask”-style blocks to capture diverse search scenarios and boost passage-level relevance.
- Use conversational tone and question-based headers to align with LLM answer patterns.
Actionable Tip: Reference how LLMs are changing behavior, 80% of users now rely on AI summaries for research and decision-making so your content should preempt and address all likely user needs in one place.
Step 3: Structuring for SGE Visibility (Snippets, FAQs, Clusters)
To win Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) and LLM inclusion, structure your content for machine and human scanning.
How to Execute:
- Use featured snippet-friendly formats: Start with clear definitions, use bullet lists, and concise tables for key information.
- Add FAQ schema and structured data to markup key sections, making it easier for Google and LLMs to extract and cite your answers.
- Organize content in clusters: Group related questions and answers together, with internal linking between cluster pages.
- Bold important entities and key concepts within passages, increasing their extractability for SGE and LLMs.
Actionable Tip: Place a TL;DR summary or “Key Takeaways” box at the top of long-form content.
Step 4: Optimizing Entities, Relations, and E-E-A-T Signals
Visibility in LLMs and SGE increasingly depends on entity clarity and your content’s trust signals.
How to Execute:
- Audit your content for entity coverage: Are all relevant concepts, brands, and people mentioned clearly and contextually?
- Use schema to reinforce relationships (Person, Organization, Product, FAQ Page).
- Add author bios, credentials, and cite real-world case studies to strengthen E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authority, Trustworthiness).
- Reference up-to-date statistics, primary sources, and industry authorities to further bolster credibility.
- Update and refresh content regularly, signaling to LLMs and Google that your information is current and reliable.
Actionable Tip: Showcase “as seen in” logos, testimonials, and external reviews within your content. This not only supports classic E-E-A-T for Google but also signals authority to LLMs parsing your expertise.
Implementing LLM SEO means shifting from “ranking for keywords” to “earning citations and summaries” inside AI-powered search. Master these four steps, and your content will not only survive the AI search revolution, it will lead it.
Conclusion: The Future of SEO Is Semantic and Strategic
The old SEO playbook keywords, backlinks, and chasing page-one spots is obsolete.
Zero-click searches dominate. LLMs like ChatGPT and Perplexity now decide what users see and trust. Google’s market share is dropping for the first time in a decade. Traditional tactics alone aren’t enough.
What matters now: semantic clarity, entity optimization, and being cited by AI not just indexed.
For founders and SEO leaders: If you want to protect your traffic and stay ahead, invest in a full LLM SEO strategy.
Strategic Next Steps:
- Audit for Semantic Gaps: Find and fix weak spots in entity coverage and structure.
- Build Authority: Prioritize depth, expert bios, and real results.
- Go Multi-Platform: Optimize for ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, and Claude not just Google.
- Prioritize Zero-Click: Make your content easy to quote and summarize.
- Monitor and Adapt: Track LLM and SGE performance, and keep refining.
The future of SEO is semantic and strategic. Adapt now or risk becoming invisible.
